In times of unexpected emergencies, having a solid foundation in first aid can mean the difference between life and death. When you offer basic medical care to someone with a physical injury until professional medical help arrives, it is known as first aid.
In this roundup, we will explore the fundamental techniques and knowledge necessary to administer effective first aid in a variety of emergencies. By understanding these principles, you can become empowered to save lives and make a positive impact in critical moments.
First aid is the initial and immediate assistance provided to someone injured or suddenly fallen ill. It is a crucial intervention performed by individuals at the scene of an accident, emergency, or health-related incident before professional medical help arrives. The primary objective of first aid is to preserve life, alleviate pain and suffering, prevent further injury or harm, and promote recovery.
“Ensure you are ready for any unforeseen situation by understanding these 3 crucial steps.“
#1 Inspect the Scene for danger
Put your safety first by thoroughly scanning the area for any potential threats like fires, falling items, or hostile people. If the surroundings are dangerous, leave the area and look for a secure location. If it’s safe, evaluate the sick or injured person’s status without moving them unless it’s required to keep them safe from harm right away.
#2 Request medical help if necessary
Instruct someone nearby to dial 911 or the local emergency services number if you think the wounded or ill individual needs medical assistance right away. Make the call yourself if you’re by yourself. Give accurate and succinct information regarding the location and the problem, and adhere to any instructions the emergency operator gives.
#3 Give assistance to the best of your ability
Stay with the sick or injured person until professional help arrives, as long as it is safe to do so. Offer reassurance if needed and help them remain calm. If you have received basic first aid training, try to check out possible injuries they may have.
Attention: Remember, if you feel that your safety is compromised at any point during the emergency, remove yourself from the situation and wait for professional help to arrive.
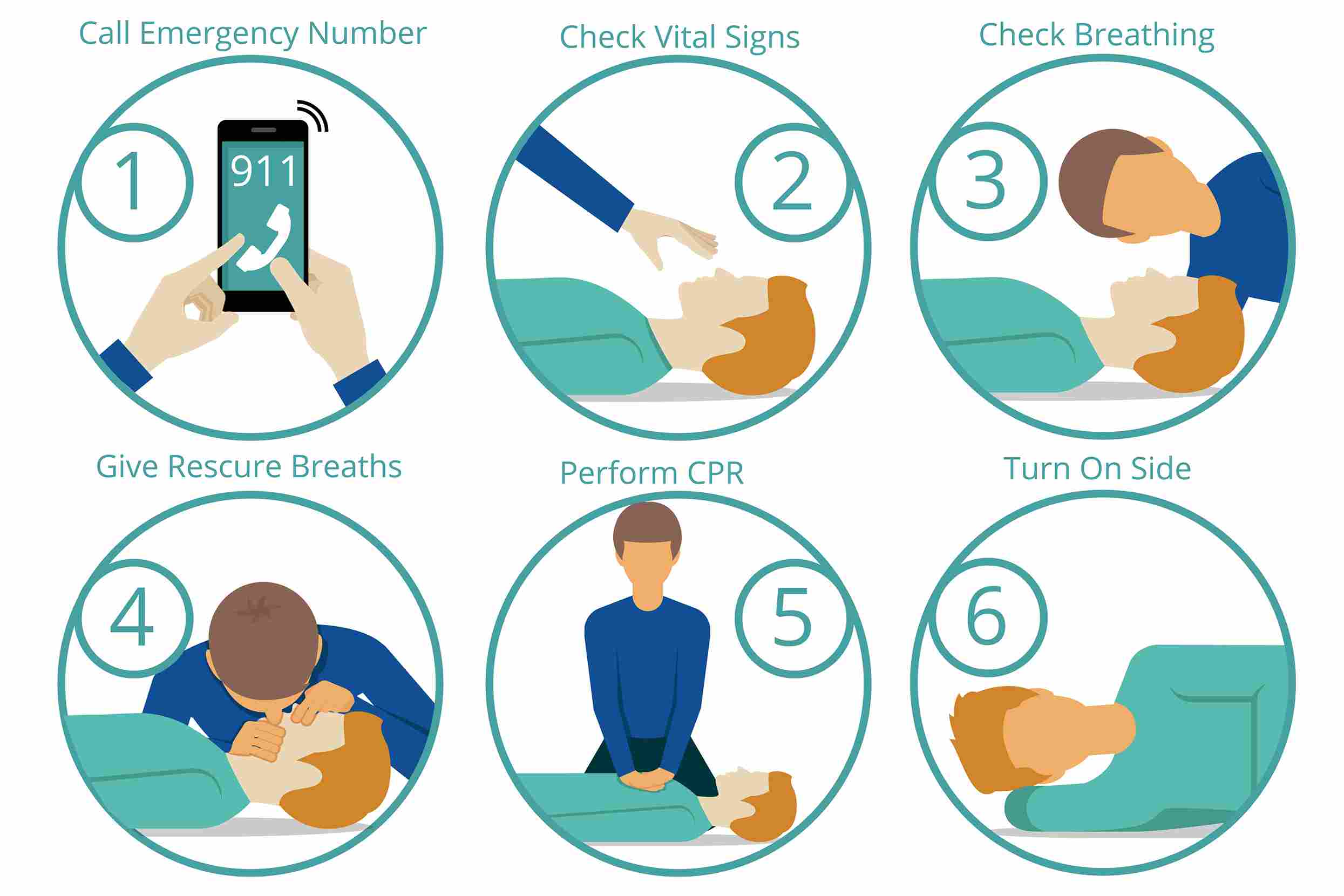
5 Lifesaving First Aid Techniques in Emergency Situations
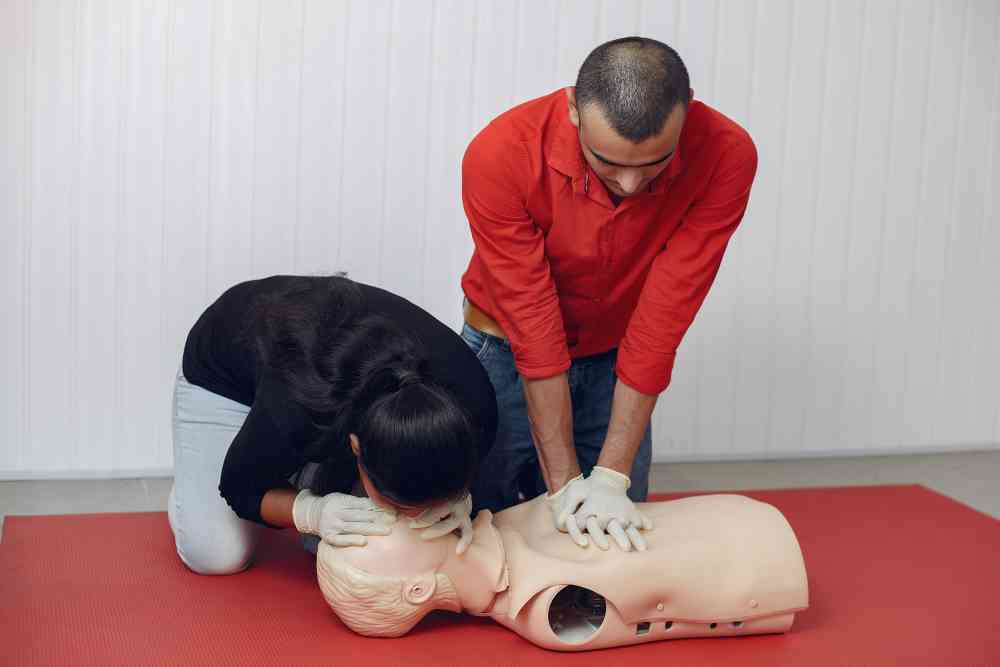
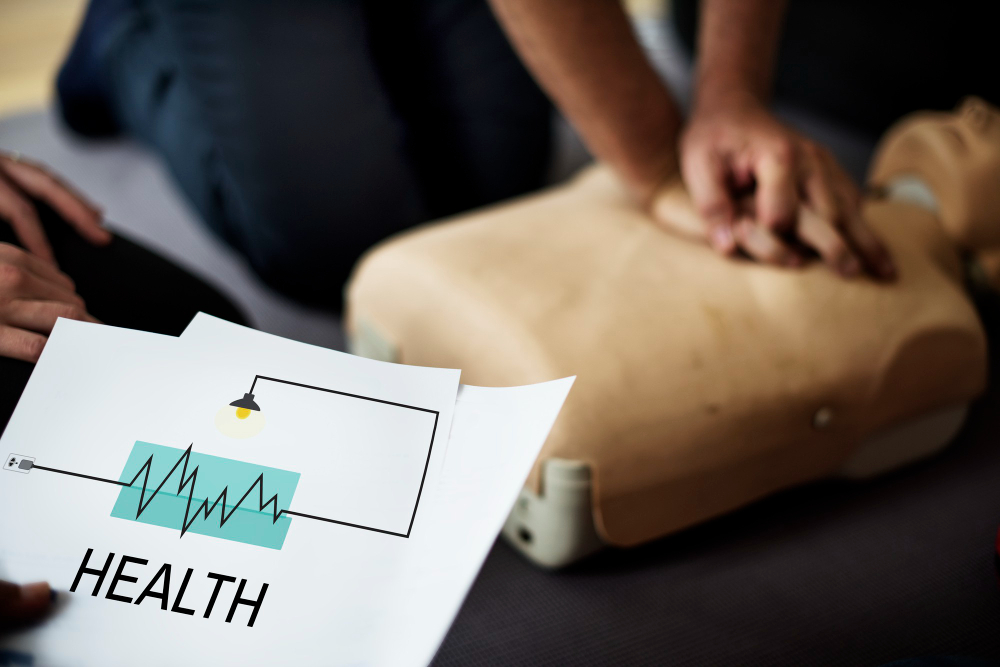
1. First aid for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR):
It is imperative to call 911 right away for emergency assistance if you see someone collapse or come across someone unconscious. Approach the unconscious person and start performing CPR if it is determined that the area is secure.
- Begin by performing chest compressions by placing the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, interlocking the other hand on top, and pushing hard and fast.
- Give rescue breaths by tilting the head back, lifting the chin, and covering the person’s mouth with yours while creating a tight seal.
- Continue cycles of 30 chest compressions followed by 2 rescue breaths until professional help arrives or the person shows signs of recovery.
It is essential to familiarize yourself with the proper techniques for providing CPR to infants and children and incorporating rescue breathing and chest compressions.
2. First aid for Severe Bleeding:
If you encounter a situation involving severe bleeding, it is crucial to take immediate action. Here’s a guide on providing first aid for severe bleeding:
Apply Pressure:
Apply direct pressure to the wound using a clean cloth, sterile dressing, or your hand. Maintain continuous pressure to help control the bleeding. If the cloth becomes soaked with blood, place another layer on top and continue applying pressure.
Elevate the Injured Area:
If possible, raise the injured limb above the level of the heart. This can help reduce blood flow to the area and aid in controlling the bleeding. However, do not elevate the limb if it causes pain or worsens the injury.
Use Pressure Points:
If direct pressure doesn’t effectively control the bleeding, apply pressure to the nearest pressure point between the bleeding site and the heart. Apply pressure with your fingers or palm until the bleeding subsides. However, avoid using this technique if you suspect a broken bone or if it causes additional pain or discomfort.
Apply Tourniquet as a Last Resort:
A tourniquet should be used as a last resort when other means cannot control severe bleeding. If necessary, apply a commercial tourniquet or use a wide, non-elastic bandage to create a makeshift tourniquet. Place it above the bleeding site, ensuring it is tight enough to stop the bleeding but not so tight that it cuts off circulation completely.

3. First Aid for Babies, kids
To be prepared for potential emergencies, it is advisable to maintain a fully stocked first aid kit in both your home and car. You can either purchase a ready-made kit or assemble one yourself.
If you have a toddler, it’s important to review the contents of a standard first aid kit and make any necessary replacements or additions with items suitable for babies. For instance, your kit should include an infant thermometer and infant-specific pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
Furthermore, storing the first aid kit in a location that is out of reach for your baby is crucial to ensuring their safety.
For more specific guidance on creating an infant-friendly first aid kit, it’s best to consult your pediatrician or family doctor, who can provide detailed information tailored to your baby’s needs.
By being prepared and having the appropriate supplies readily available, you can better respond to any unforeseen situations and provide prompt care for your little one.

4. First aid for Burns
- Ensure your safety and remove the person from the source of the burn.
- Assess the severity of the burn: first-degree (redness, pain), second-degree (blisters), or third-degree (charred skin).
- For first-degree burns, cool the area with cold running water for about 10-20 minutes.
- Cover the area loosely with a sterile, non-stick dressing for second-degree burns.
- Seek medical attention for third-degree burns immediately.
- Do not pop blisters or apply ice directly to the burn.
- Offer over-the-counter pain relief if needed and keep the person comfortable.
- Monitor for signs of infection or worsening symptoms.
5. First aid for Heart Strokes
When the body becomes excessively hot, it can lead to heat exhaustion, a condition that, if left untreated, can progress to heatstroke, a potentially life-threatening emergency.
If someone is overheating, it is important to guide them to rest in a cool area and take the following steps to help cool down their body:
– Encourage them to remove any extra layers of clothing.
– Place a cool and damp sheet over them.
– Apply a cool and wet towel to the back of their neck.
– Sponge their body with cool water.
If the individual displays signs or symptoms of heatstroke, such as nausea, confusion, fainting, seizures, or a fever of 104°F (40°C) or higher, it is critical to call 911 immediately.
If the person is conscious and not vomiting, suggest drinking small amounts of cool water or a sports drink. Familiarize yourself with additional techniques to assist in the recovery from heat exhaustion or heatstroke.
Remember, taking prompt action is essential in heat-related emergencies to ensure the person’s well-being.

What NOT To Do in First Aid
While first aid is crucial in emergencies, there are certain actions that should be avoid as they can potentially worsen the situation or cause harm. Here are some things to avoid in the name of first aid:
Performing Procedures without Proper Training:
First aid should only be administer by individuals who have receive appropriate training and certification. Attempting procedures without proper knowledge and skills can lead to unintended consequences and potentially worsen the condition of the injured or ill person.
Ignoring Personal Safety:
It is important to prioritize personal safety when providing first aid. If the situation is unsafe, such as in the presence of ongoing threats, hazardous materials, or dangerous environments, it is crucial to wait for professional help to arrive. Putting yourself at risk can create further casualties and hinder the effectiveness of first aid efforts.
Neglecting to Call for Professional Help:
While first aid is essential, it should never replace the need for professional medical assistance. Even if the initial care provided seems effective, always call for emergency medical services or go to the nearest healthcare facility for a thorough evaluation and appropriate medical treatment.
Improper Handling of Spinal Injuries:
In cases of suspected spinal injuries, it is crucial to avoid moving the person unless absolutely necessary or under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Mishandling spinal injuries can lead to further damage to the spine, potentially causing paralysis or other severe complications.
Applying Excessive Pressure or Improper Techniques:
When administering first aid, it is important to apply appropriate pressure, especially when controlling bleeding or performing chest compressions. Applying excessive force can cause harm, such as tissue damage or broken ribs. Additionally, improper techniques or devices can be ineffective or harmful, such as using makeshift tourniquets or incorrect bandaging methods.
Providing Medications without Professional Guidance:
Unless specifically trained and authorized, avoid administering medications to others, especially prescription drugs. Dosage, contraindications, and potential allergies are important considerations that should be evaluat by healthcare professionals. Encourage the person to seek medical attention for proper medication administration.
Remember, first aid is meant to provide immediate care and support until professional medical help arrives. When in doubt or faced with a complex situation, it is best to wait for professional assistance rather than taking actions that may exacerbate the situation or cause harm.
The Bottom Line
You can handle emergency situations confidently and competently by mastering first aid fundamentals. Remember, providing immediate care during critical moments can significantly improve the chances of survival and recovery. Empower yourself by learning and practicing these lifesaving techniques, as your actions may someday make all the difference in someone’s life.



Leave a Reply